Utilization of Origin Criteria
Luzon Region
Attracting Foreign Investment for Domestic FTA Case Model
Key Products of the Luzon Region
-
Key Products 1
Electronic Products Semiconductors, integrated circuits, and other electronic components.
-
Key Products 2
Machinery and Transportation Equipment Automotive parts, machinery, aircraft components, etc.
-
Key Products 3
Processed Foods A variety of processed foods and beverages.
Expected Effects
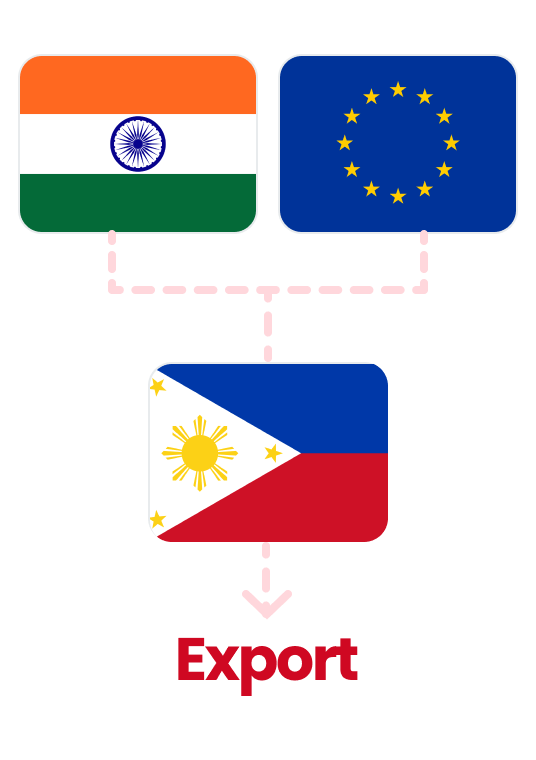
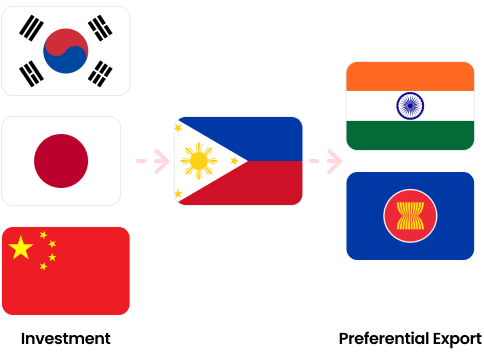
The Philippines, having established FTAs with major economic powers such as China, Japan, and South Korea, is emerging as a global FTA hub, which is expected to boost foreign investment in the country.
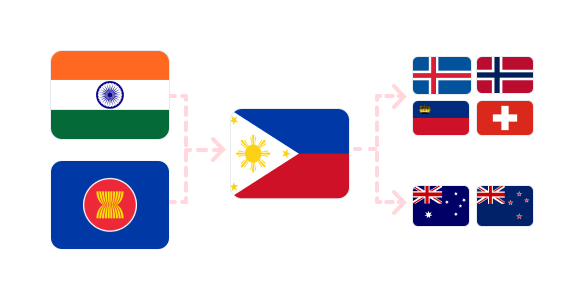
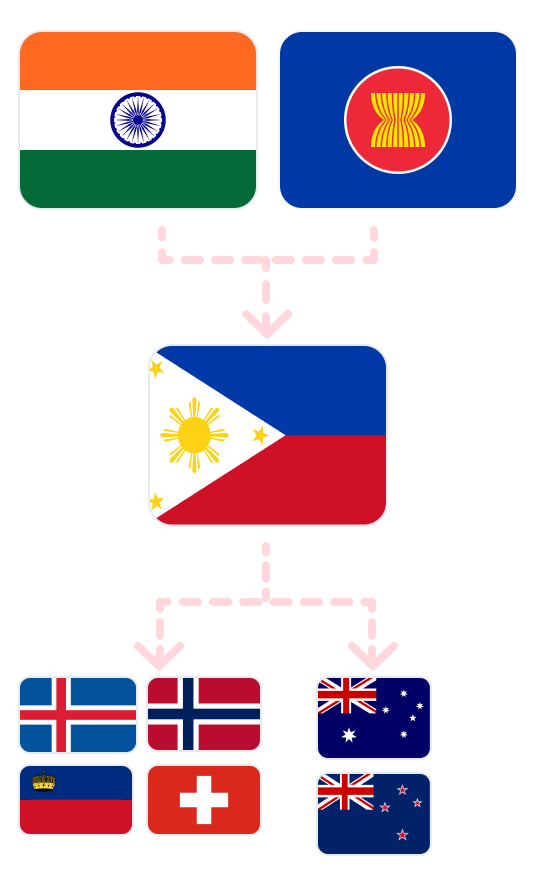
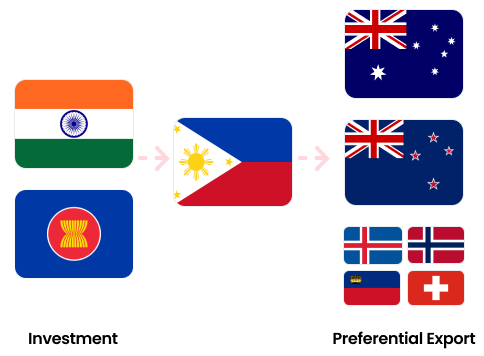
Increase interest from Indian and ASEAN companies in investing in the Philippines to leverage FTAs such as AANZFTA and PH-EFTA FTA.
-
Utilize the Philippines as a strategic entry point
-
Utilize Philippine FTA agreements
Visayas Region
Enhancing FTA Export Competitiveness Model for Agricultural and Marine Processed Products
Key Products of the Visayas Region
-
Key Products 1
Seafood Shrimp, tuna, squid, crustaceans, etc.
-
Key Products 2
Copra and Coconut Products
-
Key Products 3
Sugar
Expected Effects
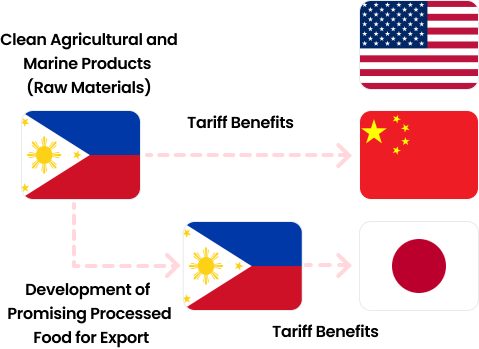
A form of importing raw materials from ASEAN, India, and other FTA partner countries, processing them, and then exporting them.
Processed food benefits from cost savings and easier origin compliance when importing raw materials for processing from FTA partner countries.
-
Model Framework 1
-
Model Framework 2
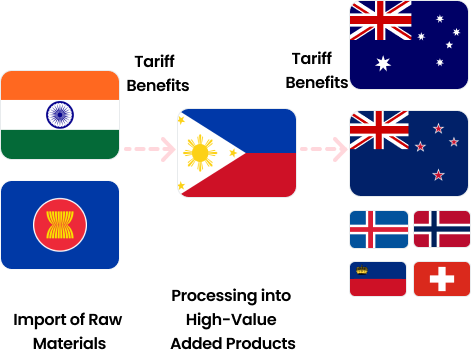
Mindanao Region
Banana-Based Product Export FTA Case Model
The Philippines can leverage its abundant agricultural resources to establish an export case model through Free Trade Agreements (FTAs). Bananas, in particular, are one of the Philippines' key agricultural products. By exporting processed banana products to FTA partner countries, the Philippines can achieve cost savings and market expansion.

Cost Reduction through Changing Raw Material Suppliers
Changing Raw Material Supply Chain
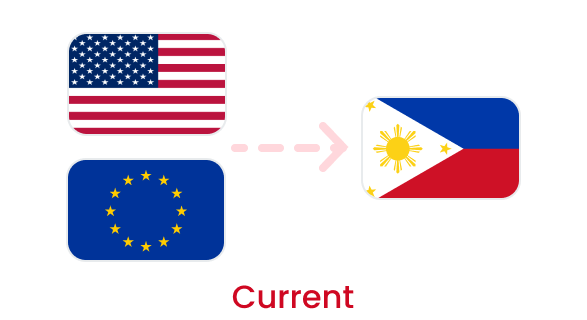
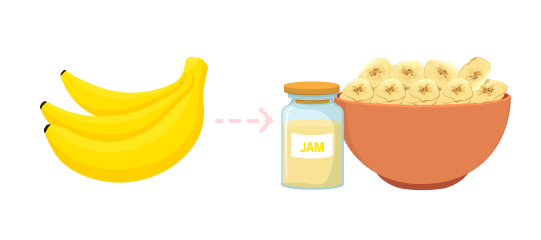
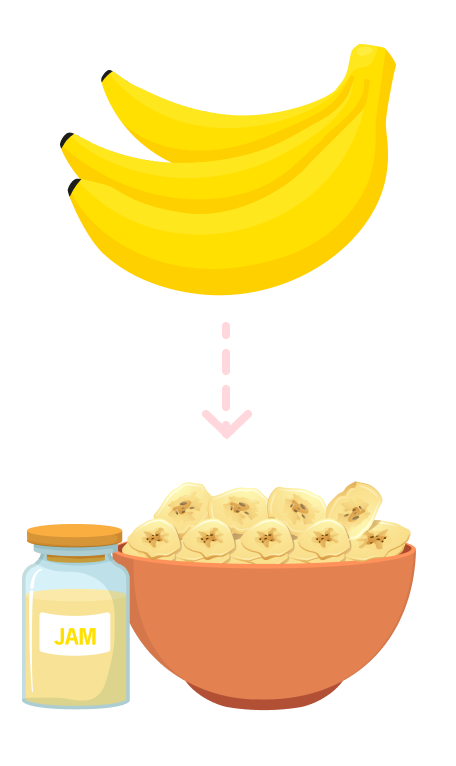
Import raw materials such as vitamins and additives from the US and Europe.
Source raw materials from ASEAN countries (e.g., Malaysia, Indonesia).


Achieve approximately 5% cost reduction.
Manufacturing Process of Processed Products
Product Banana-based products such as banana chips.
Compliance with Origin Requirements Meeting the criteria of HS 4-digit transformation and value-added standards.
Destination Countries for Export

Countries with FTA & GSP Agreements: ASEAN, South Korea, China, etc.
Applying Preferential Tariff Rates to Products from the Philippines
Meeting Origin Requirements
Using bananas from the Philippines and vitamins/additives from ASEAN countries. Meeting the criteria of HS 4-digit transformation by processing the raw materials. Creating added value through processing.
Export Tariff Benefits



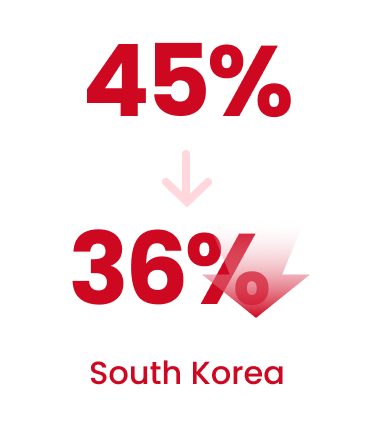

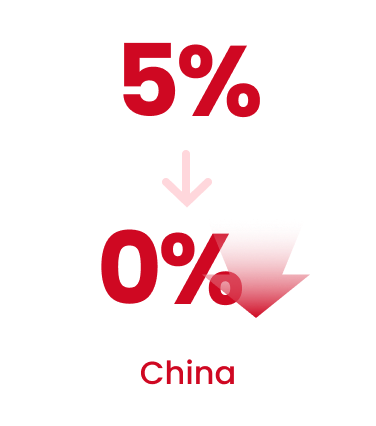
Common: Up to a 15% reduction in export unit price.
South Korea: Export tariff benefits through applying preferential tariff rates
(from a base of 45% to a preferential rate of 36%).
China: Export tariff benefits through applying preferential tariff rates (from a
base of 5% to a preferential rate of 0%).
Expected Benefits
Cost Savings
Cost savings through reduced import expenses for raw materials.
Cost savings through applying preferential tariff rates under FTA agreements for exports.
Enhanced Competitiveness
Strengthened market share through enhanced price competitiveness.
Enhanced global brand image of processed agricultural products from the Philippines.
Improved Profitability
Increased sales through cost reduction and market expansion.
Revenue diversification through exploring new export markets.
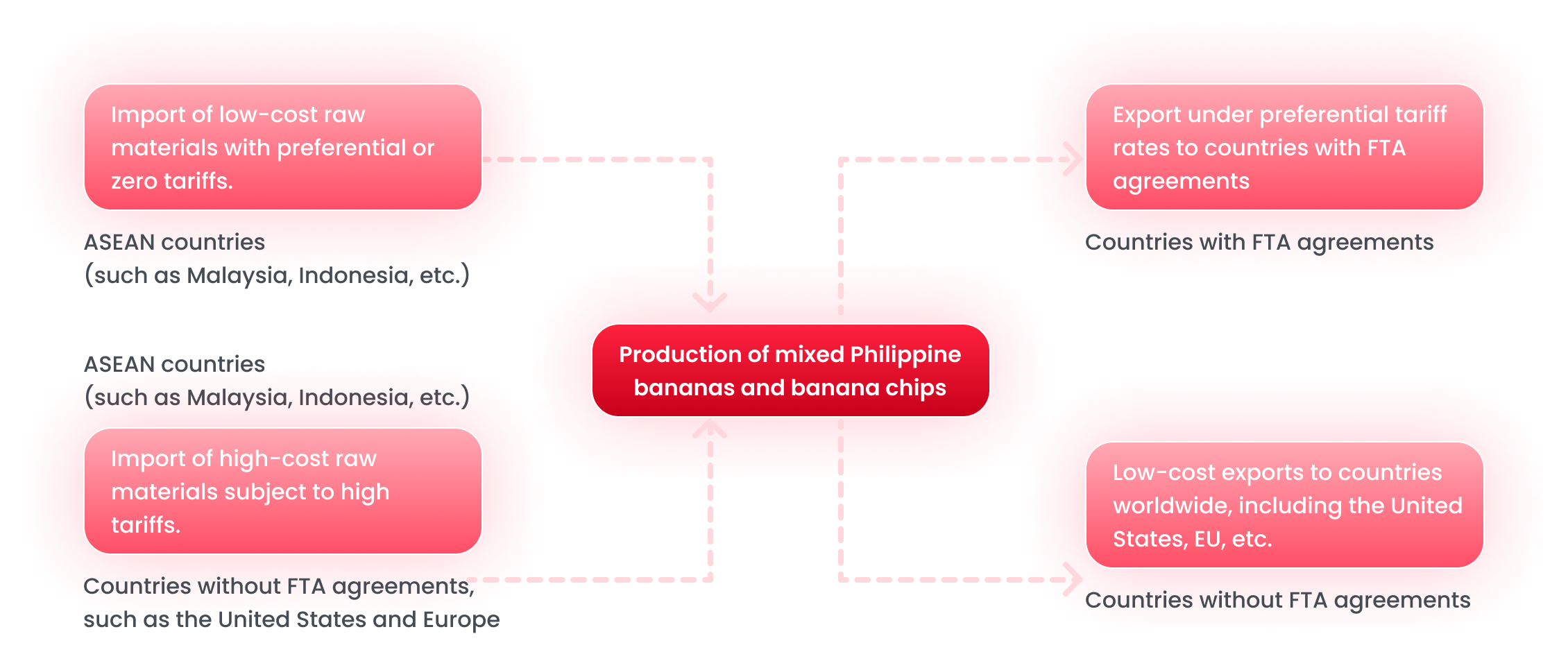
- 1. ASEAN countries(such as Malaysia, Indonesia, etc.) : Import of low-cost raw materials with preferential or zero tariffs.
- 2. ASEAN countries(such as Malaysia, Indonesia, etc.), Countries without FTA agreements, such as the United States and Europe : Import of high-cost raw materials subject to high tariffs.
- 3. Production of mixed Philippine bananas and banana chips
- 4. Low-cost exports to countries worldwide, including the United States, EU, etc. (Countries without FTA agreements)
- 5. Export under preferential tariff rates to countries with FTA agreements (Countries with FTA agreements)