Overview of the CANADA-GSP Case Model
Canada's Generalized System of Preferences (GSP) is a trade program that provides tariff exemptions on certain products to developing countries to promote economic growth. Established in 1974, the program currently offers GSP tariff benefits to the Philippines.
Reduced or eliminated tariffs on eligible products imported from designated developing countries.
A broad array of products, including agricultural goods, industrial products, textiles, and clothing, qualify for GSP benefits.
To qualify, products must meet specific rules of origin, ensuring a significant portion of the product's value is added in the beneficiary developing country.
Overview of Global Cumulation
Ex-factory Price of Goods
Originating outside a GPT beneficiary country or Canada
Originating from GPT beneficiary countries or Canada
To qualify for GPT treatment, up to 40% of the ex-factory price of goods packed for shipment to Canada may originate outside a GPT beneficiary or Canada. This means that at least 60% of the ex-factory price must originate in one or more GPT beneficiary countries or Canada. The 60% qualifying content may be accumulated from various GPT beneficiary countries or Canada. However, any parts, materials, or inputs used in the production of the goods that have entered the commerce of a non-beneficiary country lose their GPT originating status.
All GPT beneficiary countries are regarded as one single area. Therefore, to calculate GPT originating content, all value-added and manufacturing processes performed in the GPT area may be cumulated as the originating content. Also, any Canadian originating content can be regarded as GPT content. The goods must be finished in the GPT beneficiary country in the form in which they are imported into Canada.
Conditions for Recognizing the Origin of Goods under Canada's GSP
Identification
Verification of GSP-Eligible Items in the Canada Agreement
Requirements
Cost of Non-Originating Materials / EX-Factory Price = In cases where it exceeds 40%
criteria
If MC40 is not met, use cumulative criteria
GSP Sample Model
To produce aircraft engines, raw materials are imported from Cambodia, Vietnam, and Malaysia. The final production of the aircraft engines is then manufactured in the Philippines, and the aircraft engines produced are exported to Canada. Since all three countries, Cambodia, Vietnam, and Malaysia, are GPT beneficiaries, the value of the raw materials imported from these three countries can be added to the work performed in the Philippines to ensure that the radio meets the 60% origin content requirement.
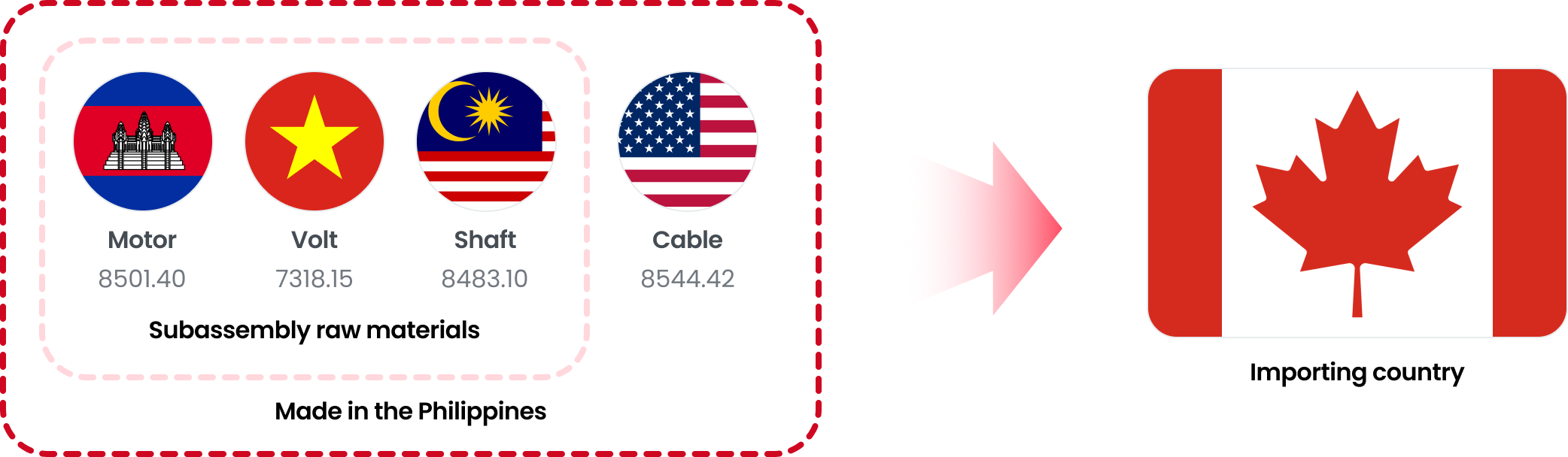
| Raw material | HS Code | Origin | Price(USD) | Cumulative or not |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Motor | 8501.40 | Cambodia | 500 | yes |
| Volt | 7318.15 | Vietnam | 50 | yes |
| Shaft | 8483.10 | Malaysia | 150 | yes |
| Cable | 8544.42 | USA | 100 | no |
| Total cost of materials from origin | 700 | |||


| Raw material | HS Code | Origin | Price(USD) | Cumulative or not |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Motor | 8501.40 | China | 500 | no |
| Volt | 7318.15 | Japan | 50 | no |
| Shaft | 8483.10 | Korea | 150 | no |
| Cable | 8544.42 | USA | 100 | no |
| Total cost of materials from origin | yes | |||






