Process of FTA utilization when importing
Effective FTA
To utilize an FTA when importing, it is necessary to verify that FTA has been signed and is in
effect between the Philippines and the exporting country.
The countries with effective FTAs can be checked below.
Item Classification

Advisor
When it's difficult to classify an HS code, you can refer to the following.
Advanced Ruling of Tariff CommissionTariff Benefit
After finding the item number of the imported goods, it is necessary to check whether there are FTA tariff benefits in Philippines.
You can check the FTA rate in the respective country's agreement text, and refer to the following tariff table:
- When importing to our country from FTA partner countries: Refer to the tariff schedule of the Philippines.
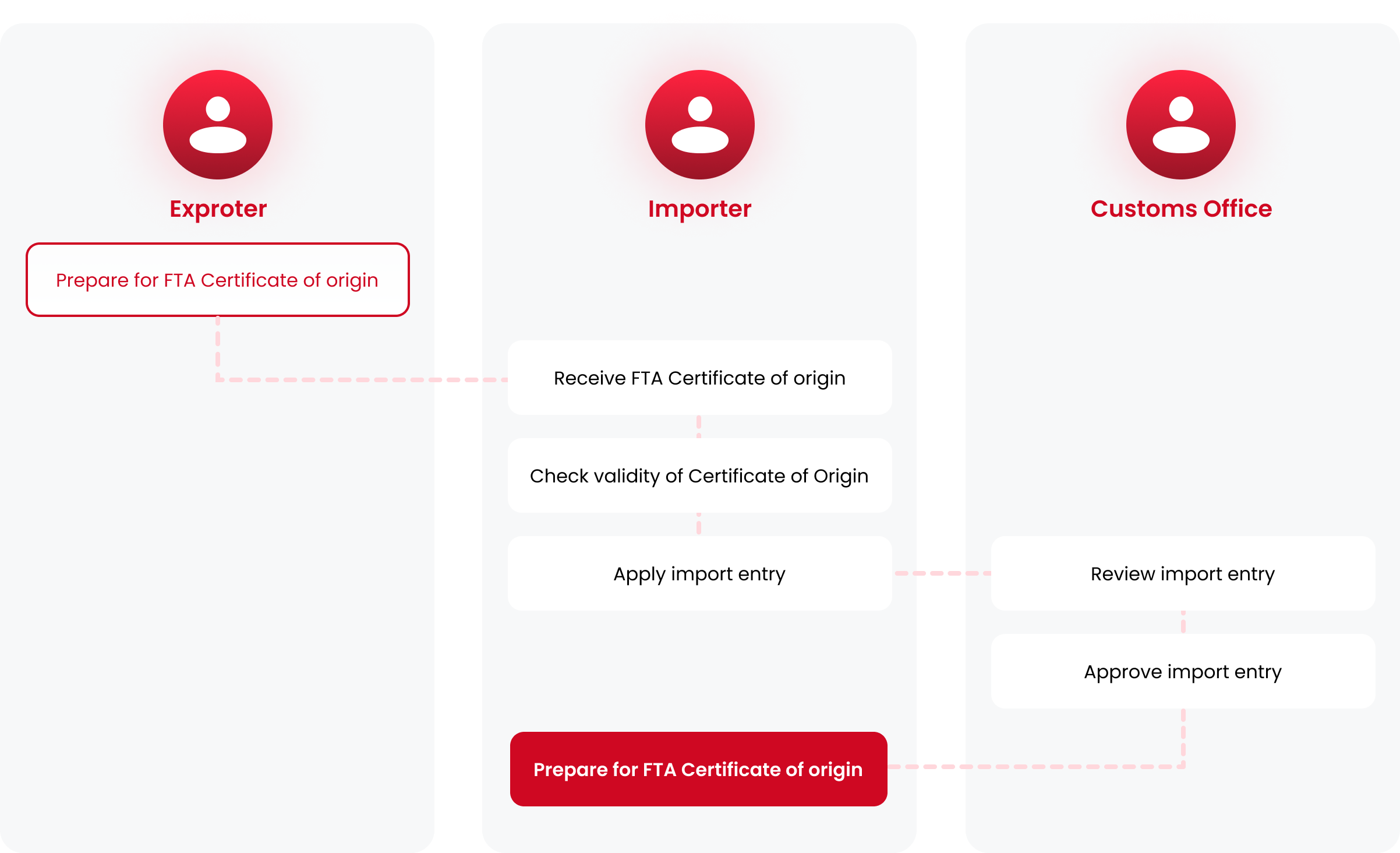
Obtain FTA Certificate of Origin
Applying FTA tariff rates upon importation is only possible when a valid FTA certificate is received
from the exporter.
It is necessary to verify in advance whether exporters are aware of the FTA agreement forms,
as only certificates of origin issued in accordance with the methods stipulated in each agreement
are valid for application.
The issuance method of the Certificate of Origin varies according to each agreement as below.
ATIGA (ASEAN Trade in Goods Agreement)
- Method of Issuance
- Issued by the authority
- Validity Period
- 12 months
- Retroactive Issuance
- 1 year from date of shipment
ACFTA (ASEAN-China Free Trade Area)
- Method of Issuance
- Issued by the authority
- Validity Period
- 1 Year
- Retroactive Issuance
- 12 months from shipment
Form AKFTA (ASEAN-Korea Free Trade Agreement)
- Method of Issuance
- Issued by the authority
- Validity Period
- 1 Year
- Retroactive Issuance
- 1 year from date of shipment
AIFTA (ASEAN-India Free Trade Area)
- Method of Issuance
- Issued by the authority
- Validity Period
- 12 months
- Retroactive Issuance
- 12 months from shipment
AJCEP (ASEAN-Japan Comprehensive Economic Partnership)
- Method of Issuance
- Issued by the authority
- Validity Period
- 1 Year
- Retroactive Issuance
- 1 year from date of shipment
PJEPA (Philippines-Japan Economic Partnership Agreement)
- Method of Issuance
- Issued by the authority
- Validity Period
- 6 months
- Retroactive Issuance
- -
PH-EFTA (Philippines-European Free Trade Association)
- Method of Issuance
- Self-issuance
- Validity Period
- 12 months
- Retroactive Issuance
- -
AHFTA (ASEAN-Hong Kong, China Free Trade Agreement)
- Method of Issuance
- Issued by the authority
- Validity Period
- 1 year
- Retroactive Issuance
- 1 year from date of shipment
AANZFTA (ASEAN-Australia-New Zealand Free Trade Agreement)
- Method of Issuance
- Self-issuance
- Validity Period
- 12 months
- Retroactive Issuance
- 12 months from date of exportation
RCEP (Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership)
- Method of Issuance
- Issued by the authority Self-issuance (Not in effect)
- Validity Period
- 1 year
- Retroactive Issuance
- 1 year from date of shipment
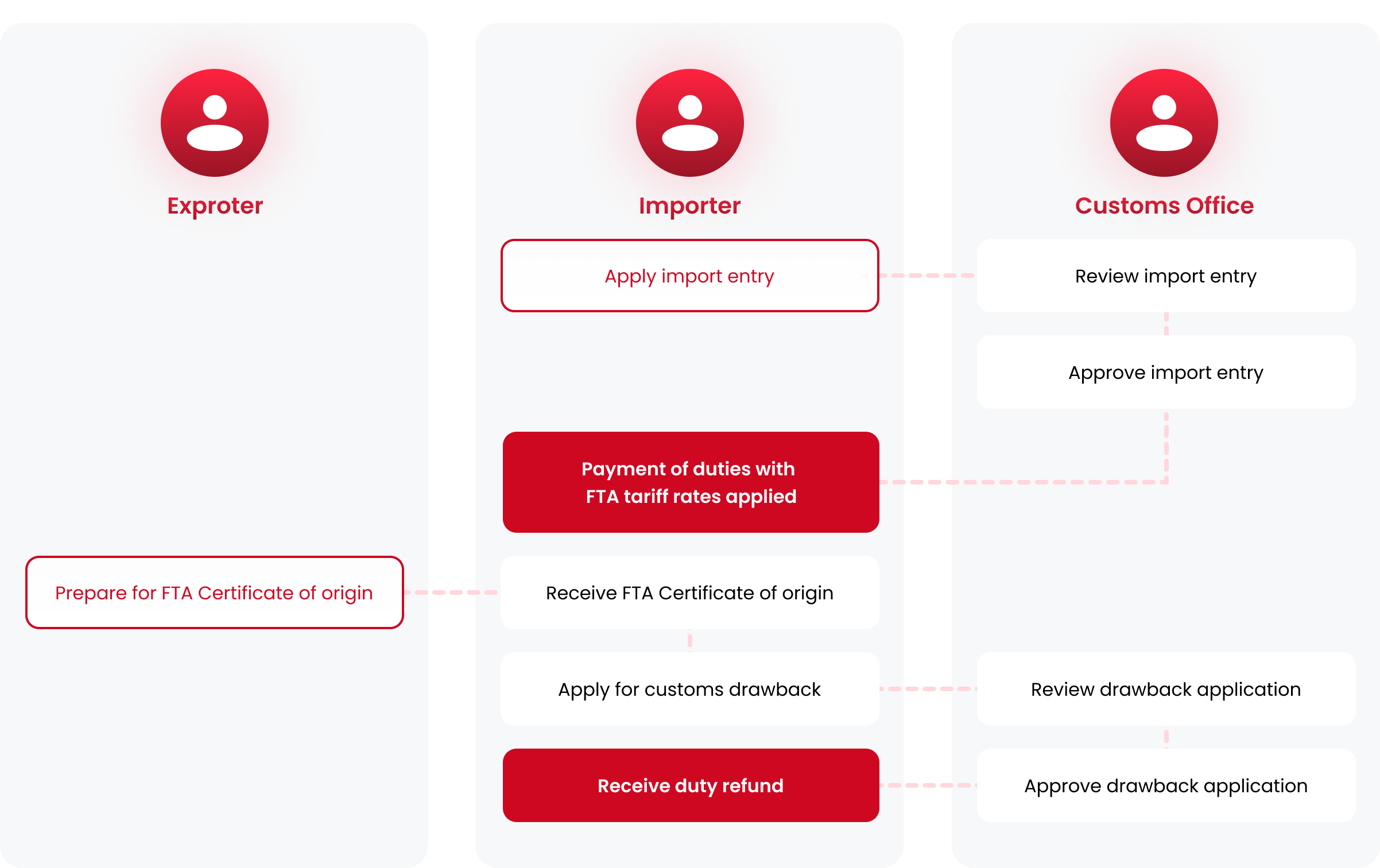
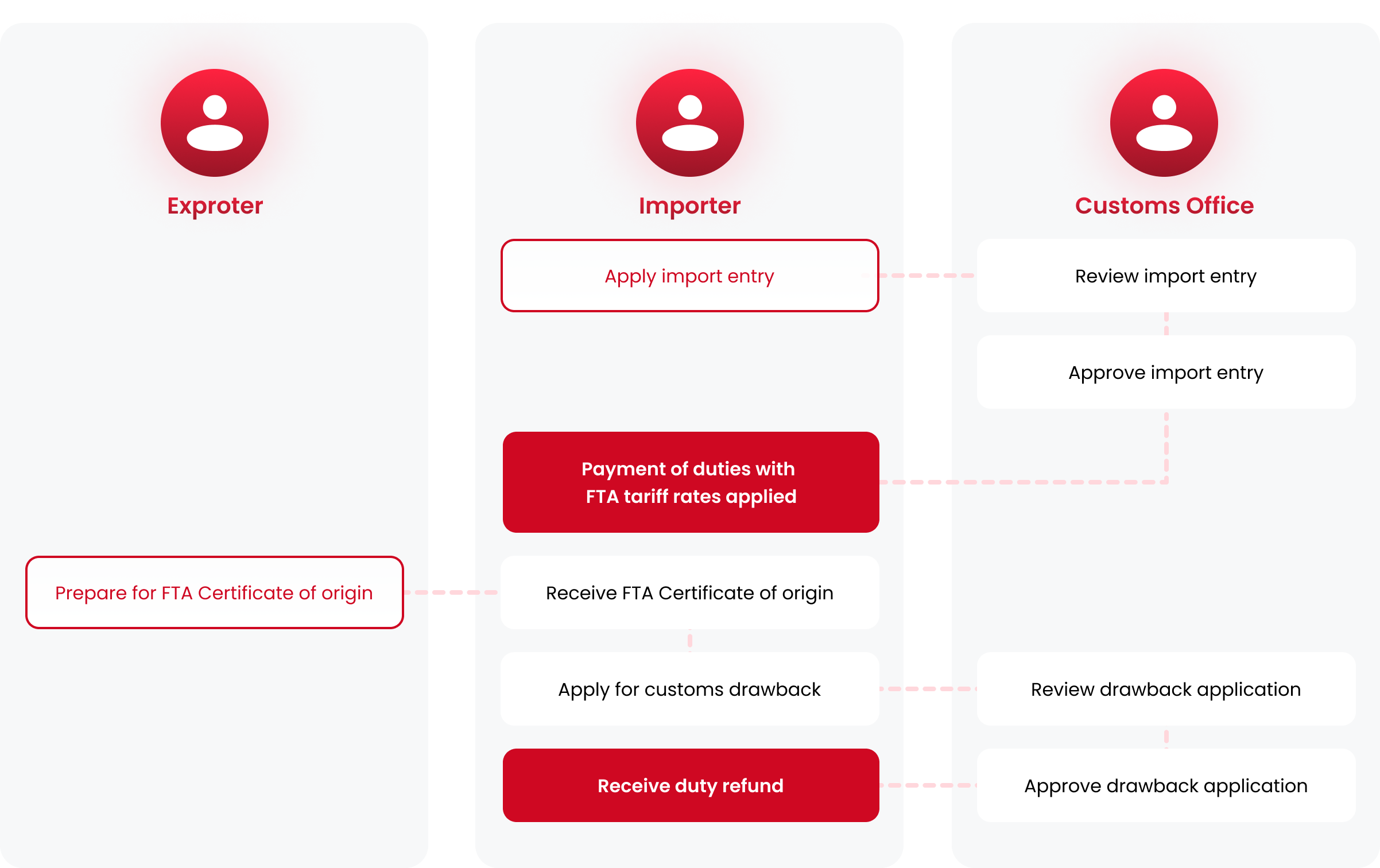
Apply for FTA tariff rate
Apply for FTA tariff rate to receive FTA tariff rates, importers must submit an import entry to apply
FTA tariff rate When making an import declaration,
application for preferential tariff treatment can be made before or after customs clearance.
In case of post application of FTA, customs drawback can be made by importers within 1 year of the importation.
Process for preferential tariff treatment of pre-clearance
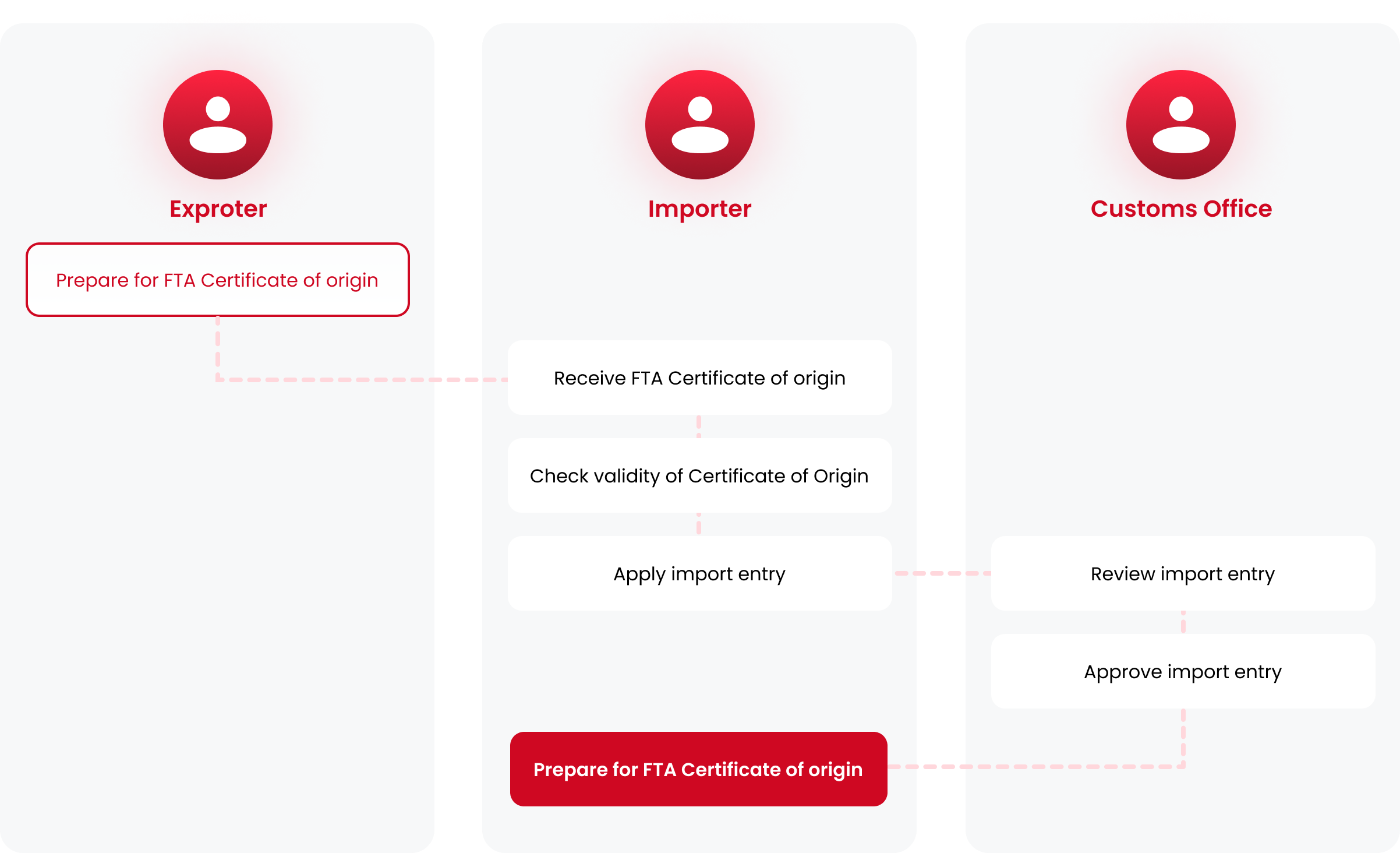
Process of preferential tariff treatment of post-clearance
Maintain data keeping requirement

- Records Keeping Period
- Importers are required to keep all records for a period of 3 years from
the date of final payment of duties and taxes or customs clearance by
below regulation.
Supporting Provision : Requirement to Keep Records
(Sec. 1003, An act modernizing the customs and tariff administration)
Term of Importer
(1) Importer-of-record or consignee, owner or declarant, or a party who :
- (i) Imports goods into the Philippines or withdraws such goods into the Philippine customs territory for consumption or warehousing; files a claim for refund or drawback; or transports or stores such goods carried or held under security; or
- (ii) Knowingly causes the importation or transportation or storage of imported goods referred to above, or the filing of refund or drawback claim.
(2) An agent of any party described in paragraph (1)or(3) A person whose activities require the filing of a goods declaration.
* A person ordering imported goods from a local importer or supplier in a domestic transaction shall be exempted from the requirements imposed by this section unless:
- 1 The terms and conditions of the importation are controlled by the person placing the order; or
- 2 The circumstances and nature of the relationship between the person placing the order and the importer or supplier are such that the former may be considered as the beneficial or true owner of the imported goods; or
- 3 The person placing the order had prior knowledge that they will be used in the manufacture or production of the imported goods.
- Penalty
- Failure to keep the records required by this Act shall constitute a waiver of this right to contest the results of the audit based on records kept by the Bureau.





