Case model explanation utilizing rules of origin
Advantages of the Philippines
If exports happens to below countries…
ATIGA, RCEP
AKFTA, RCEP, PKFTA
AJEPA, PJEPA, RCEP
ACFTA, RCEP
Signing Various agreements with one country as Philippine or ASEAN
Creates an opportunity to enhance the utility and flexibility of the agreements
Case Model for Comparative Origin Criteria between FTA agreements
The Philippines, being a member of ASEAN, has engaged in various Free Trade Agreement (FTA) negotiations either as part of ASEAN or independently. This diversity can be leveraged for beneficial outcomes.
PSR
Product Specific Rules
PASSThe most critical aspect in determining the origin as PHILIPPINE lies in assessing whether the criteria for origin determination on a PSR (Product Specific Rules) are met.
By comparing and analyzing the origin criteria across agreements concluded with a single trading partner, favorable criteria for origin determination can be chosen, enabling the issuance of a Certificate of Origin as below example.
Example
Export Destinations
Korea
Main Export Products
Processed Food
HS CODE
2106.90
Tariff Rate
MFN Product Specific Rules
8%
AK-FTA ASEAN-Korea Free
Trade Agreement
0%
RCEP Product Specific Rules
6.4%
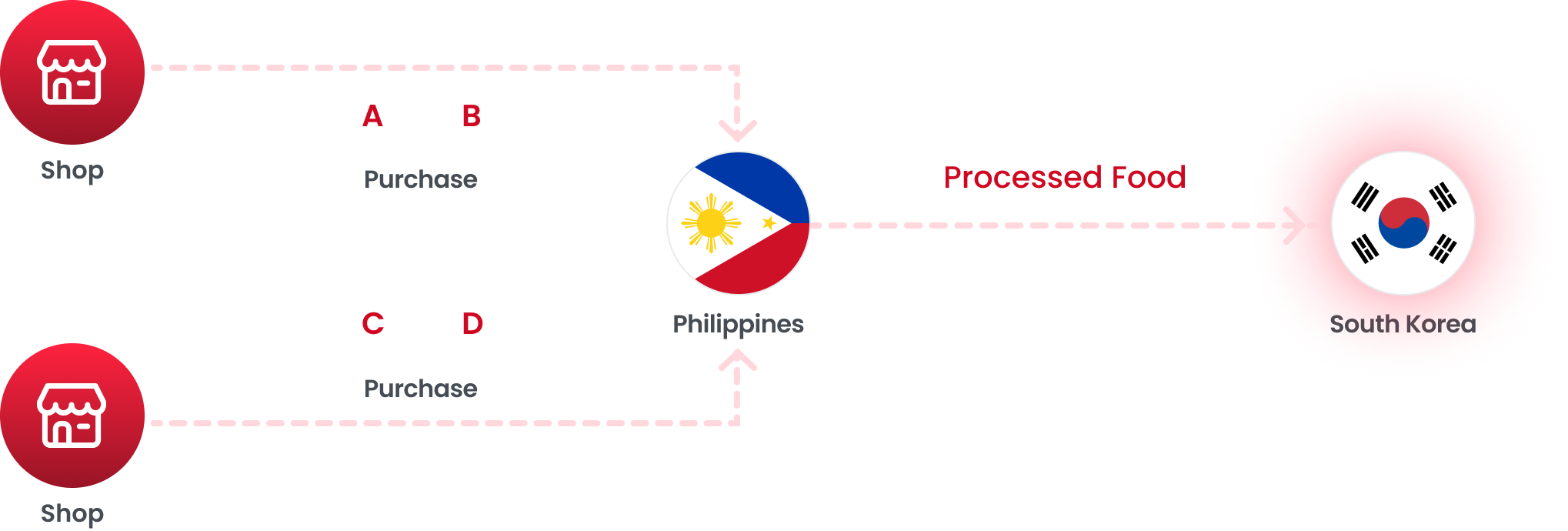
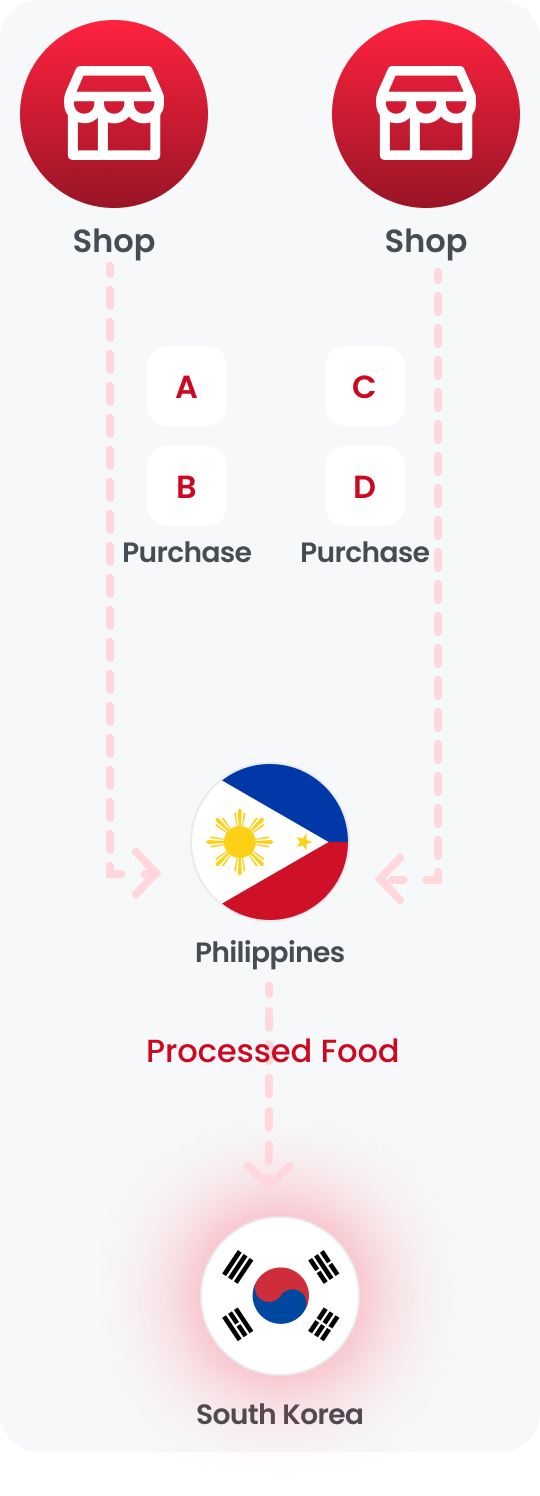
The Philippines utilizes two agreements with Korea: the Korea-ASEAN and
RCEP.
Comparing the PSRs of each agreement yields the following results.
AKFTA
- Condition 1
- RVC 40% Regional Value Content (RVC) The percentage of a product's value that must come from within the region to qualify for preferential treatment under a trade agreement.
- Condition 2
- WO (HS 1211.20, 1212.21, 1302.14, 1302.19) Wholly Obtained (WO) Refers to goods that are entirely produced or obtained within a single country, often used in determining the origin of agricultural or natural products.
- Condition 3
- Conditions 1 and 2 must be met simultaneously
RCEP
- Condition 1
- RVC 40%
- Condition 2
- CTH Change of Tariff Heading (CTH) A rule that requires a product to undergo a change in tariff classification at the heading (four-digit) level to qualify as originating under a trade agreement.
- Condition 3
- Condition 1 or 2 must be met
BOM (Bill of Materials)
A
-
 Raw Material
Raw Material
-
HS Code 1211.20
Origin ZZ
Amount 3.5
B
-
 Raw Material
Raw Material
-
HS Code 1211.20
Origin ZZ
Amount 3.5
C
-
 Raw Material
Raw Material
-
HS Code 1211.20
Origin ZZ
Amount 3.5
D
-
 Raw Material
Raw Material
-
HS Code 1211.20
Origin ZZ
Amount 3.5
Originating Materials 9 Originating Materials B (PH, 6) C (PH, 3) Total : 6 + 3 = 9
EXW 9.5
Non-originating 5.5 Non-originating A (ZZ, 3.5) D (ZZ, 2) Total : 3.5 + 2 = 5.5
FOB 10
Origin Determination
AKFTA
- Condition 1
- BD method : (10,000-5,500)/10,000 = 45% Pass
- Condition 2
- 1211.20 cannot meet WO criteria Non-Pass
- Condition 3
- As a result, example product does not meet origin criteria of AKFTA PSR
RCEP
- Condition 1
- BD method : (10,000-5,500)/10,000 = 45% Pass
- Condition 2
- 1211.20 cannot meet WO criteria Pass
- Condition 3
- Example product meet either origin criteria of RCEP PSR
As a result, AKFTA Certificate of Origin can not be issued but RCEP Certificate of Origin
can be issued.
Buyers can benefit from tariff savings using RCEP certificate of
origin.





